ZexCora
Derived from the Latin word cora, meaning "heart" or "core," ZexCora serves as the central hub of our platform. It is responsible for fundamental exchange functionalities, such as the matching engine and maintaining user balances and states.
To optimize system performance and accessibility, ZexCora operates with two types of nodes:
Light Node: Light nodes are responsible for maintaining the system state and tracking transactions that alter the state. Anyone can read the state from any light node.
Full Node: Full nodes, in addition to maintaining records, can process external requests and transactions. Running a full node requires more resources than a light node due to the additional responsibilities.
ZexCora Architecture
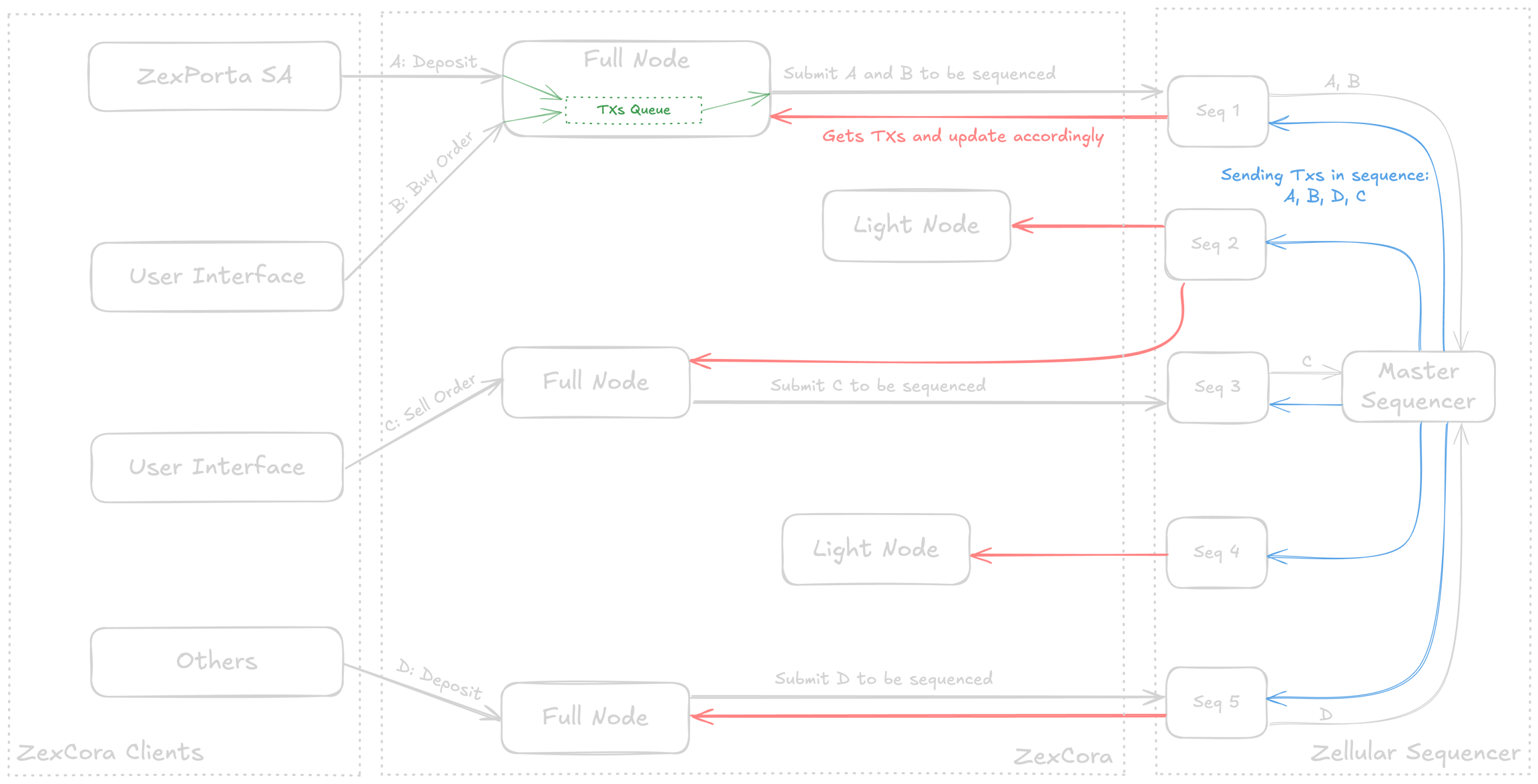
The ZexCora platform employs a robust system to process transactions efficiently and securely. Below is a step-by-step explanation of how the architecture handles transactions:
Transaction Submission Transactions are initiated by ZexPorta SA, user interfaces (UI), or other external sources acting as ZexCora clients. These transactions, such as deposits, buy orders, and sell orders, are sent to ZexCora Full Nodes.
Processing by Full Nodes The Full Nodes receive the transactions, place them in a transaction queue. Full Nodes then prepare the transactions to be forwarded to the Sequencer for ordering.
Forwarding to Sequencer Nodes Full Nodes send the transactions to one of the Sequencer Nodes in the Zellular Sequencer. These Sequencer Nodes collect transactions for ordering and send them to the Master Sequencer.
Global Ordering by Master Sequencer The Master Sequencer collects transactions from all Sequencer Nodes and organizes them into a single, definitive sequence. For example, if transactions A, B, C, and D are received, the Master Sequencer may arrange them as A, B, D, C. The ordered sequence is then broadcast to all nodes within the Zellular Sequencer.
Verification by Light Nodes ZexCora Light Nodes receive the sequenced transactions and verify their integrity and validity. Light Nodes ensure the transactions are consistent with the current system state.
Validation by Full Nodes Verified transactions are collected by Full Nodes for detailed validation. Each transaction is checked for source authenticity and applicability to the current system state. For example, in a withdrawal transaction, the system checks if the user has sufficient funds available.
Transaction Execution Once validated, the transactions are forwarded to the Matching Engine and executed:
For deposits and withdrawals, the user’s balance is updated.
For buy and sell orders, based on the order price, the transactions are registered in an order book or executed instantly.
This step-by-step architecture ensures secure, transparent, and efficient transaction processing within the ZexCora platform.
Transaction Data Formats
The following tables outline the data format for all transaction types.
1. Registration Transaction
version
Request version; 1 in this instance
1 byte
name
rfor REGISTER
1 byte
public
Public key of the sender
33 bytes
sig
Signature from the sender
64 bytes
Total Length
Depends on the length of the message.
99 bytes
The sender should sign the follwing massege:
2. Order Transaction
version
Request version; 1 in this instance
1 byte
name
bfor BUY or sfor SELL
1 byte
base_token_len
Lenght of Base token identifier
1 byte
quote_token_len
Lenght of Base Quote token identifier
1 byte
base_token
Base token identifier
Variable
quote_token
Quote token identifier
Variable
amount
Order amount
8 bytes
price
Price per unit
8 bytes
t
Timestamp
4 bytes
nonce
Unique transaction identifier
4 bytes
public
Public key of the sender
33 bytes
sig
Signature from the sender
64 bytes
Total Length
Total length depends on base_token and quote_token length.
Variable
The sender should sign the follwing massege:
3. Cancellation Transaction
version
Request version; 1 in this instance
1 byte
name
cfor CANCEL
1 byte
order_tx
Variable
public
Public key of the sender
33 bytes
sig
Signature from the sender
64 bytes
Total Length
Minimum length is 99 bytes (header + slice + public key).
Variable
The sender should sign the follwing massege:
4. Deposit Transaction
version
Request version; 1 in this instance
1 byte
name
dfro DEPOSIT
1 byte
token_chain
Chain identifier for the token
3 bytes
deposit_count
Number of deposits included in the current transaction
2 bytes
Decoded Message
Per Deposit
Variable
tx_hash
Deposit transaction hash
66 bytes
token
The address of deposited token
42 bytes
value
Deposit amount
32 bytes
decimals
The decimals of deposited token
1 byte
block_timestamp
Time of deposit
4 bytes
user_id
User identifier
8 bytes
internal_tx_number
Number of internal transation (in case deposit occurs in a transaction with multiple intenal transaction) or the output number (e.g. for Bitcoin)
1 byte
For the Whole Batch Deposit Request
frost_sig
FROST group signature
32 bytes
ecdsa_sig
ECDSA signature
132 bytes
Total Length
Total length is calculated based on the deposit-specific message size.
Variable
The sender should sign the encoded message that is described above.
5. Withdrawal Transaction
version
Request version; 1 in this instance
1 byte
name
wfro WITHDRAWAL
1 byte
token_len
Lenght of the Token identifier
1 byte
token_chain
Chain identifier for the token
3 bytes
token_name
Token identifier
Variable
amount
Amount to withdraw
8 bytes
destination
Destination address
20 bytes
t
Timestamp
4 bytes
nonce
Unique transaction identifier
4 bytes
public
Public key of the sender
33 bytes
sig
Signature from the sender
64 bytes
Total Length
Total length depends on token_name length.
Variable
The sender should sign the follwing massege: